Cet article est le dernier de la série concernant l’API Northwind.
Prérequis : Maitrise du Framework ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model.
Pour rappel, l’objectif était le suivant :
- Ajouter un champs « Commentaire » au sein de l’objet RAP qu’il sera possible de modifier (Partie I)
- Créer une entité fille « Commandes » qui représentera les commandes associées a ces produits
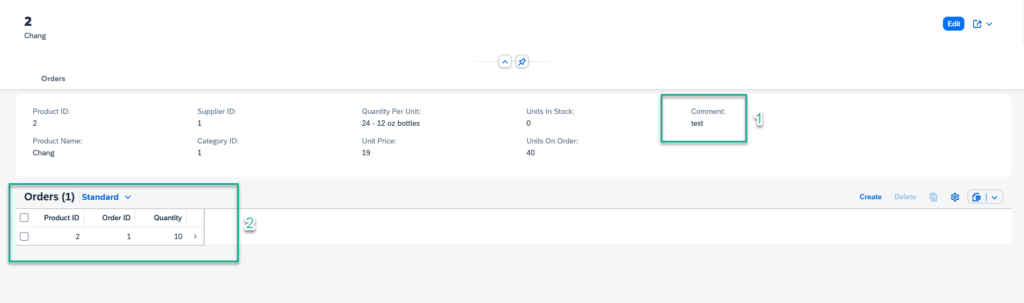
Dans notre dernier article, nous avions ajouté un champs à l’entité PRODUCT.
Ici, nous allons créer une nouvelle entité, qui correspondra aux commandes liées aux produits disponible dans l’API Northwind. Nous allons ensuite lier ces 2 entités pour permettre aux utilisateurs de créer facilement des commandes associées à ces produits via une application Fiori.
Tout le code contenant la Partie I et la Partie II est disponible sur notre GitLab.
1/ Créer une table de base de données et la CDS associée
@EndUserText.label : 'Order Northwind'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table ztest_order {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key product_id : abap.int4 not null;
key order_id : abap.int4 not null;
quantity : abap.int4;
}Le champs product_id permettra de faire le lien avec les données retournées de l’API.
Les champs order_id et quantity stockeront les données relatives aux commandes ( order_id sera un id généré automatiquement par le Business Object RAP )
@AbapCatalog.viewEnhancementCategory: [#NONE]
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: 'Order association product Northwind'
@Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true
@ObjectModel.usageType:{
serviceQuality: #X,
sizeCategory: #S,
dataClass: #MIXED
}
define view entity ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND_ORDER
as select from ztest_order
association to parent ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND as _Product on $projection.product_id = _Product.product_id
{
@EndUserText.label: 'Product ID'
@UI.facet: [ {
label: 'General Information',
id: 'GeneralInfo',
purpose: #STANDARD,
position: 10 ,
type: #IDENTIFICATION_REFERENCE
} ]
@UI.identification: [ {
position: 10
} ]
@UI.lineItem: [ {
position: 10
} ]
@UI.selectionField: [ {
position: 10
} ]
key product_id,
@EndUserText.label: 'Order ID'
@UI.identification: [ {
position: 20
} ]
@UI.lineItem: [ {
position: 20
} ]
@UI.selectionField: [ {
position: 20
} ]
key order_id,
@EndUserText.label: 'Quantity'
@UI.identification: [ {
position: 30
} ]
@UI.lineItem: [ {
position: 30
} ]
@UI.selectionField: [ {
position: 30
} ]
quantity,
_Product
}
Comme nous voulons relier les commandes aux produits associés, nous ajoutons une association to parent entre la CDS qui représente les commandes (ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND_ORDER) et celle qui représente les produits (ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND).
De plus, comme il s’agit d’une CDS entity et non d’une custom CDS entity, alors il n’y a pas besoin de gérer manuellement la récupération des données. C’est fait par le framework.
2/ Modifier la custom CDS produit
Il suffit d’ajouter la composition vers ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND_ORDER
@EndUserText.label: 'test custom CDS Northwind'
@ObjectModel.query.implementedBy: 'ABAP:ZTEST_CRT_PROXY'
@UI.headerInfo: { typeName: 'Product', typeNamePlural: 'Products', title: { type: #STANDARD, value: 'product_id' }, description.value : 'product_name' }
define root custom entity ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND
{
@UI.facet: [
{ id: 'Product', purpose: #STANDARD, type: #IDENTIFICATION_REFERENCE, position: 10 },
{ id: 'Order', purpose: #STANDARD, type: #LINEITEM_REFERENCE, label: 'Orders', position: 20, targetElement: 'orders' }
]
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 10 }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 10 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Product ID'
key product_id : int4;
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 20 }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 20 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Product Name'
product_name : abap.char( 100 );
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 30 }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 30 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Supplier ID'
supplier_id : int4;
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 40 }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 40 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Category ID'
category_id : int4;
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 50 }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 50 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Quantity Per Unit'
quantity_per_unit : abap.char( 100 );
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 60 }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 60 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Unit Price'
unit_price : abap.dec( 16, 0 );
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 70}]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 70 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Units In Stock'
units_in_stock : int2;
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 80, label: 'Units On Order' }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 80 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Units On Order'
units_on_order : int2;
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 90, label: 'Comment' }]
@UI.identification: [{ position: 90 }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Comment'
comment_product : abap.char(100);
orders : composition [0..*] of ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND_ORDER;
}
3/ Modifier le behavior definition
unmanaged implementation in class zbp_test_cust_northwind unique;
//strict ( 2 ); //Uncomment this line in order to enable strict mode 2. The strict mode has two variants (strict(1), strict(2)) and is prerequisite to be future proof regarding syntax and to be able to release your BO.
define behavior for ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND //alias <alias_name>
late numbering
//lock master
//authorization master ( instance )
//etag master <field_name>
{
//create;
update;
//delete;
field ( readonly ) product_id, category_id, product_name, quantity_per_unit, unit_price, units_in_stock, units_on_order, supplier_id;
association orders { create; }
}
define behavior for ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND_ORDER //alias <alias_name>
//late numbering
//lock dependent by _Product
//authorization dependent by _Product
//etag master <field_name>
{
// create;
update;
delete;
field ( readonly ) product_id, order_id;
association _Product;
mapping for ztest_order
{
product_id = product_id;
order_id = order_id;
quantity = quantity;
}
}On ajoute les informations liées à l’entité COMMANDE.
Comme on veut pouvoir, créer, modifier ou supprimer une commande, on ajoute CREATE-BY-ASSOCIATION (ici, on ne veux autoriser la création d’une commande que depuis un article – il faut accéder à l’article pour créer la commande – On aurait pu ajouter CREATE si on souhaiter donner l’autorisation de crée une commande sans partir d’un article, ici c’est juste un choix pour montrer comment on peut intéragir entre les 2 entités), UPDATE, DELETE.
Enfin, on note que le late numbering est activé, ce qui va nous permettre de gérer la génération automatique de l’id de la COMMANDE (order_id) dans la méthode « ADJUST_NUMBER ».
4/ Modifier le Behavior Implementation
Nous allons modifier le behavior implementation développé dans la classe zbp_test_cust_northwind
CLASS lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND DEFINITION INHERITING FROM cl_abap_behavior_handler.
PUBLIC SECTION.
TYPES : BEGIN OF ty_buffer,
pid TYPE abp_behv_pid,
product_ID TYPE ztest_cust_northwind_order-product_ID,
order_id TYPE ztest_cust_northwind_order-order_id,
quantity TYPE ztest_cust_northwind_order-quantity,
END OF ty_buffer,
BEGIN OF ty_buffer_prod,
product_ID TYPE ztest_cust_northwind-product_ID,
comment_product TYPE ztest_cust_northwind-comment_product,
END OF ty_buffer_prod.
CLASS-DATA : mt_buffer_create TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF ty_buffer WITH EMPTY KEY.
CLASS-DATA : mt_buffer_update TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF ty_buffer WITH EMPTY KEY.
CLASS-DATA : mt_buffer_delete TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF ty_buffer WITH EMPTY KEY.
CLASS-DATA : mt_buffer_upd_prod TYPE STANDARD TABLE OF ty_buffer_prod WITH EMPTY KEY.
PRIVATE SECTION.
METHODS read FOR READ
IMPORTING keys FOR READ ztest_cust_northwind RESULT result.
METHODS rba_Orders FOR READ
IMPORTING keys_rba FOR READ ztest_cust_northwind\Orders FULL result_requested RESULT result LINK association_links.
METHODS cba_Orders FOR MODIFY
IMPORTING entities_cba FOR CREATE ztest_cust_northwind\Orders.
METHODS update FOR MODIFY
IMPORTING entities FOR UPDATE ztest_cust_northwind.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD read.
* To implement
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD rba_Orders.
* To implement
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD cba_Orders.
DATA n TYPE i VALUE 1.
LOOP AT entities_cba INTO DATA(ls_entity).
LOOP AT ls_entity-%target INTO DATA(ls_target).
APPEND VALUE #(
pid = n
product_id = ls_target-product_id
quantity = ls_target-quantity
) TO lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_create.
APPEND VALUE #(
%cid = ls_target-%cid
%pid = n
product_id = ls_target-product_id ) TO mapped-ztest_cust_northwind_order.
n = n + 1.
ENDLOOP.
ENDLOOP.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD update.
LOOP AT entities INTO DATA(ls_entity).
APPEND VALUE #(
product_id = ls_entity-product_id
comment_product = ls_entity-comment_product
) TO lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_upd_prod.
APPEND VALUE #(
product_id = ls_entity-product_id ) TO mapped-ztest_cust_northwind.
ENDLOOP.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND_ORDER DEFINITION INHERITING FROM cl_abap_behavior_handler.
PRIVATE SECTION.
DATA : lt_buffer TYPE TABLE OF ztest_order.
METHODS update FOR MODIFY
IMPORTING entities FOR UPDATE ztest_cust_northwind_order.
METHODS delete FOR MODIFY
IMPORTING keys FOR DELETE ztest_cust_northwind_order.
METHODS read FOR READ
IMPORTING keys FOR READ ztest_cust_northwind_order RESULT result.
METHODS rba_Product FOR READ
IMPORTING keys_rba FOR READ ztest_cust_northwind_order\_Product FULL result_requested RESULT result LINK association_links.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND_ORDER IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD update.
LOOP AT entities INTO DATA(ls_entity).
APPEND VALUE #(
product_id = ls_entity-product_id
order_id = ls_entity-order_id
quantity = ls_entity-quantity
) TO lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_update.
APPEND VALUE #(
product_id = ls_entity-product_id
order_id = ls_entity-order_id ) TO mapped-ztest_cust_northwind_order.
ENDLOOP.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD delete.
LOOP AT keys INTO DATA(ls_key).
APPEND VALUE #(
product_id = ls_key-product_id
order_id = ls_key-order_id
) TO lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_delete.
APPEND VALUE #(
product_id = ls_key-product_id
order_id = ls_key-order_id ) TO mapped-ztest_cust_northwind_order.
ENDLOOP.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD read.
DATA : orders TYPE TABLE OF ztest_order.
LOOP AT keys INTO DATA(ls_key).
SELECT SINGLE * FROM ztest_order
WHERE product_id = @ls_key-product_id AND order_id = @ls_key-order_id
INTO @DATA(ls_result).
IF sy-subrc <> 0.
READ TABLE lt_buffer INTO ls_result WITH KEY product_id = ls_key-product_id order_id = ls_key-order_id.
ENDIF.
IF ls_result IS NOT INITIAL.
APPEND CORRESPONDING #( ls_result MAPPING TO ENTITY ) TO result.
ENDIF.
ENDLOOP.
IF result IS INITIAL.
APPEND VALUE #(
product_id = ls_key-product_id
order_id = ls_key-order_id
%fail-cause = if_abap_behv=>cause-not_found ) TO failed-ztest_cust_northwind_order.
ENDIF.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD rba_Product.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS lsc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND DEFINITION INHERITING FROM cl_abap_behavior_saver.
PROTECTED SECTION.
METHODS finalize REDEFINITION.
METHODS check_before_save REDEFINITION.
METHODS save REDEFINITION.
METHODS cleanup REDEFINITION.
METHODS cleanup_finalize REDEFINITION.
METHODS adjust_numbers REDEFINITION.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS lsc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD finalize.
* To implement
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD check_before_save.
* To implement
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD save.
LOOP AT lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_create INTO DATA(ls_buffer_create).
DATA(ls_data) = VALUE ztest_order( product_id = ls_buffer_create-product_id order_id = ls_buffer_create-order_id quantity = ls_buffer_create-quantity ).
MODIFY ztest_order FROM @ls_data.
ENDLOOP.
LOOP AT lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_update INTO DATA(ls_buffer_update).
ls_data = VALUE ztest_order( product_id = ls_buffer_update-product_id order_id = ls_buffer_update-order_id quantity = ls_buffer_update-quantity ).
MODIFY ztest_order FROM @ls_data.
ENDLOOP.
LOOP AT lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_delete INTO DATA(ls_buffer_delete).
DATA(ls_key) = VALUE ztest_order( product_id = ls_buffer_delete-product_id order_id = ls_buffer_delete-order_id ).
DELETE ztest_order FROM @ls_key.
ENDLOOP.
LOOP AT lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_upd_prod INTO DATA(ls_buffer_upd_prod).
DATA(ls_data_prod) = VALUE ztest_prod( product_id = ls_buffer_upd_prod-product_id comment_product = ls_buffer_upd_prod-comment_product ).
MODIFY ztest_prod FROM @ls_data_prod.
ENDLOOP.
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD cleanup.
* To implement
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD cleanup_finalize.
* To implement
ENDMETHOD.
METHOD adjust_numbers.
LOOP AT lhc_ZTEST_CUST_NORTHWIND=>mt_buffer_create ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<ls_buffer>).
SELECT MAX( order_id )
FROM ztest_cust_northwind_order
WHERE product_id = @<ls_buffer>-product_id
INTO @DATA(lv_orderid).
lv_orderid = lv_orderid + 1.
APPEND VALUE #(
%pid = <ls_buffer>-pid
%tmp = VALUE #( product_id = <ls_buffer>-product_id )
product_id = <ls_buffer>-product_id
order_id = lv_orderid ) TO mapped-ztest_cust_northwind_order.
<ls_buffer>-order_id = lv_orderid.
ENDLOOP.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.1 : Implémenter les méthodes UPDATE, DELETE
On vient créer des entrées dans le buffer ( Ici la variable mt_buffer_update et mt_buffer_delete ) et elles seront sauvegardées plus tard dans la phase de sauvegarde.
On vient également logger les instances modifiées dans le parameter MAPPED
2 : Implementer la méthode CREATE-BY-ASSOCITION (cba_Orders)
Ici, on vient créer des entrées dans le buffer ( mt_buffer_create ) et elles seront sauvegardées plus tard dans la phase de sauvegarde.
On vient également logger les instances crées dans le parameters MAPPED
- %CID va permettre de retourner les données crées dans la réponse API (en faisant le lien entre les données entrées et le PID généré)
- %PID est nécessaire car il n’y a pour le moment pas de clés transactionelles unique puisque le champs order_id va être déterminé plus tard dans la méthode ADJUST_NUMBER.
- Plus d’infos sur les implicit parameters ici
3 : Implementer la méthode ADJUST_NUMBER
On vient lire les lignes crées et on attribut un id unique pour chaque order_id relié à un produit.
On MAPPE ensuite ce nouvel ID en le reliant au %PID précédemment créé avec le nouvel order_id dans le parameter MAPPED.
4 : On update la méthode SAVE
Dans la methode SAVE, on vient traiter les demandes de CREATE-BY-ASSOCIATION/UPDATE/DELETE de notre entité ( donc l’ajout/modification/suppression d’une commande ).
C’est a ce moment qu’on vient mettre a jour la base de données.
5/ Exposer le business object RAP via une API
Créer le Service Definition et le Service Binding
On pourra ensuite utiliser cette API dans une application Fiori dont voici le résultat :
