In our last article, we saw how entity tables would allow us to simplify the creation of our CDS by combining the functionalities of classic DDIC tables and CDS into a single object.
However, we noted that it was still impossible to create modification operations on these Business Objects via RAP.
- It is now possible to implement and develop transactional operations using RAP with table entities, and to call this object via EML in ABAP programs or via OData in Fiori/Web API applications.
- We will also look at the limitations we encountered during our tests.
- In this example, we will revisit the case we developed and which can be viewed on our GitLab.
Changes made to these objects are also available in a new repository.
I. Create the BDEFs
As a reminder, our example represented the different orders received by a bakery.
To do this, we first tried using the RAP Generator Object as seen in a previous article, but it seems that it is not yet possible to perform these creations automatically at this time.
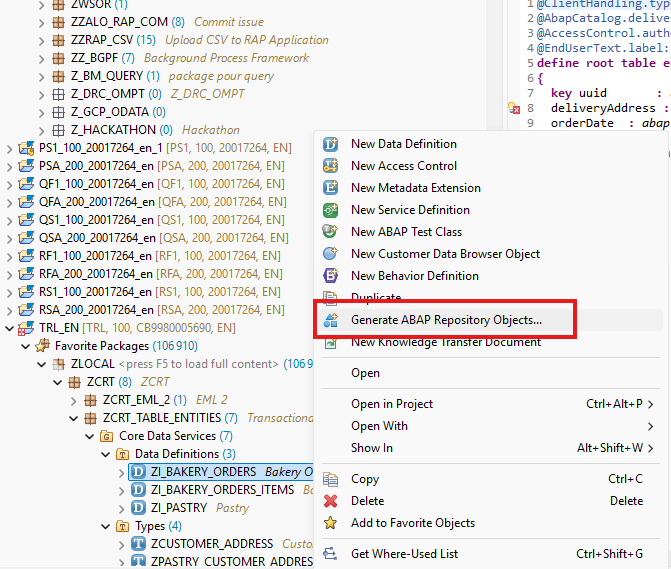
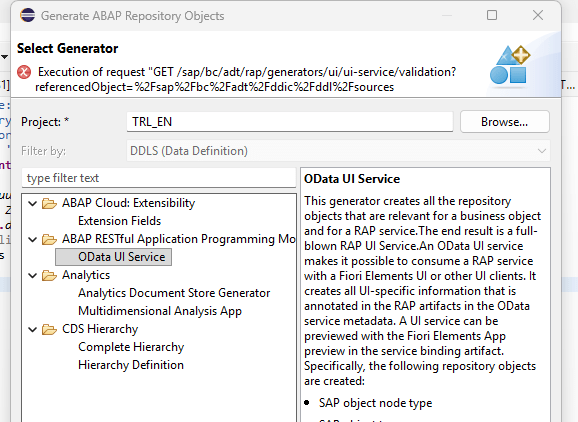
We therefore manually create the two BDEFs we need to represent our orders and the associated items.
To simplify the example, we do not add the association with the entity table representing the pastries listed in the bakery, but we will address this topic in a future article discussing cross associations, which are now available in RAP.
managed implementation in class zbp_i_bakery_orders unique;
strict ( 2 );
//with cross associations;
define behavior for ZI_BAKERY_ORDERS //alias <alias_name>
lock master
authorization master ( instance )
//etag master <field_name>
{
create ( authorization : global );
update;
delete;
field ( readonly ) uuid;
field ( numbering : managed ) uuid;
association _bakeryOrdersItems { create; }
}
define behavior for ZI_BAKERY_ORDERS_ITEMS //alias <alias_name>
lock dependent by _bakeryOrders
authorization dependent by _bakeryOrders
//etag master <field_name>
{
update;
delete;
field ( readonly ) uuid, item;
//, pastryid;
field ( numbering : managed ) item;
association _bakeryOrders;
// association _pastry abbreviation pastry
// {
// create;
// link action link_pastry;
// unlink action unlink_pastry;
// inverse function inverse_function;
// }
}Here we can see that we have the definitions of the necessary operations.
Since each command line is identified by a unique UUID, we generate it automatically via numbering (managed).
The same applies to the UUID of items (each referenced item has a UUID from a command to its own unique UUID).
We have also enabled create-by-association on our composition.
As with any other managed RAP object, it is then possible to add validations, determinations, authorization checks, actions, etc.
Note:
- As seen in the documentation: We did not enable drafts on this RAP object because entity tables do not yet support this feature. However, it would have been possible to manually create a table that could be used to save drafts.
- We had to replace the enum type in our ZC_BAKERY_ORDERS_ITEMS entity table because it was not supported.
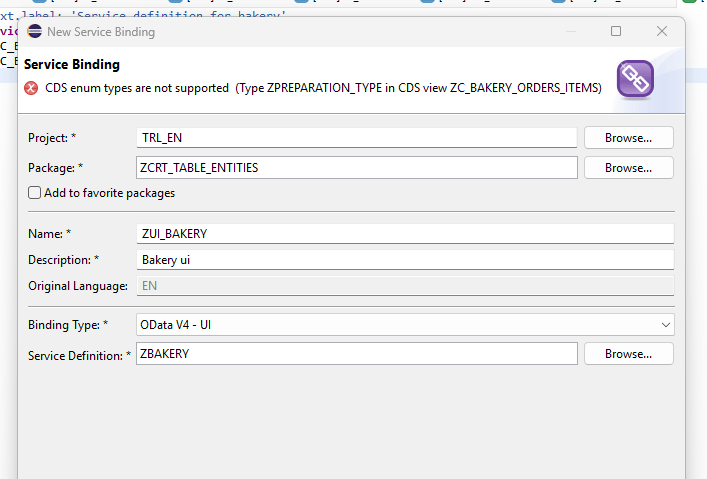
II. Tests
1. EML tests
We have created a small test case here that shows that after creating this RAP object, we can interact with the BO via EML.
CLASS zcl_test_table_entities DEFINITION
PUBLIC
FINAL
CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES if_oo_adt_classrun .
PROTECTED SECTION.
PRIVATE SECTION.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS zcl_test_table_entities IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD if_oo_adt_classrun~main.
DATA lt_test TYPE TABLE FOR CREATE zi_bakery_orders.
DATA lt_orders TYPE TABLE FOR CREATE zi_bakery_orders.
DATA lt_items TYPE TABLE FOR CREATE zi_bakery_orders\_bakeryOrdersItems.
" Create parent order
lt_orders = VALUE #(
( %cid = '1'
deliveryAddress = '1 rue du test - Lille'
orderDate = '20251001'
%control = VALUE #( deliveryAddress = if_abap_behv=>mk-on
orderDate = if_abap_behv=>mk-on )
)
).
" Create child items via association
lt_items = VALUE #(
( %cid_ref = '1'
%target = VALUE #(
( %cid = '1-1'
quantity = 2
unit = 'PC'
amount = 10
currency = 'EUR'
pastryid = '1111'
%control = VALUE #( quantity = if_abap_behv=>mk-on
unit = if_abap_behv=>mk-on
amount = if_abap_behv=>mk-on
currency = if_abap_behv=>mk-on
pastryid = if_abap_behv=>mk-on )
)
)
)
).
MODIFY ENTITIES OF zi_bakery_orders
ENTITY zi_bakery_orders
CREATE FROM lt_orders
ENTITY zi_bakery_orders
CREATE BY \_bakeryOrdersItems
FROM lt_items
FAILED DATA(lt_failed)
REPORTED DATA(lt_reported)
MAPPED DATA(lt_mapped).
COMMIT ENTITIES.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.- Via a create operation: we create an order
- Via a create-by-entity operation: We create an item on demand.
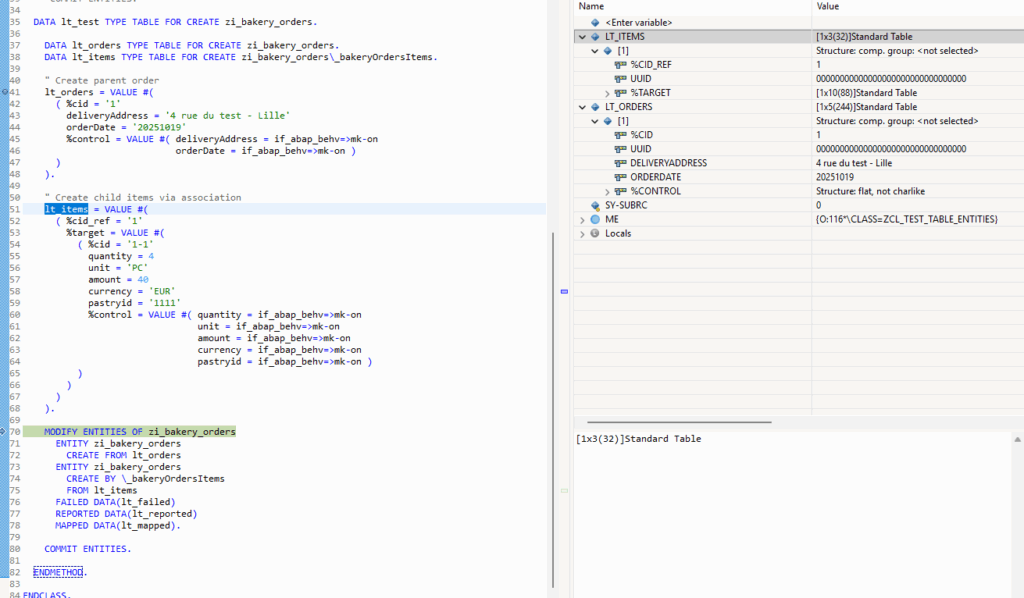
This data is now stored in CDS entities.
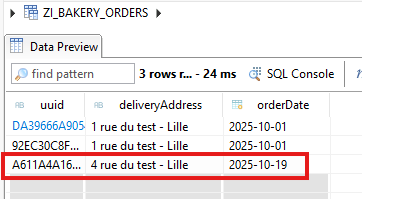
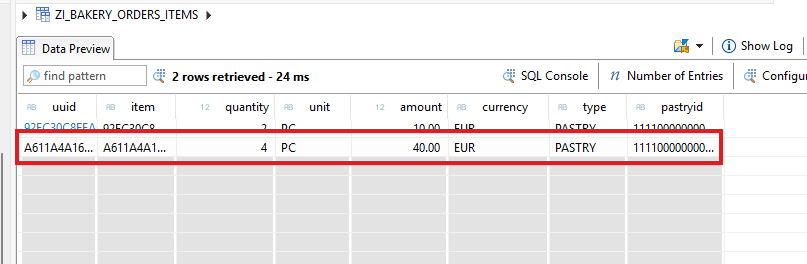
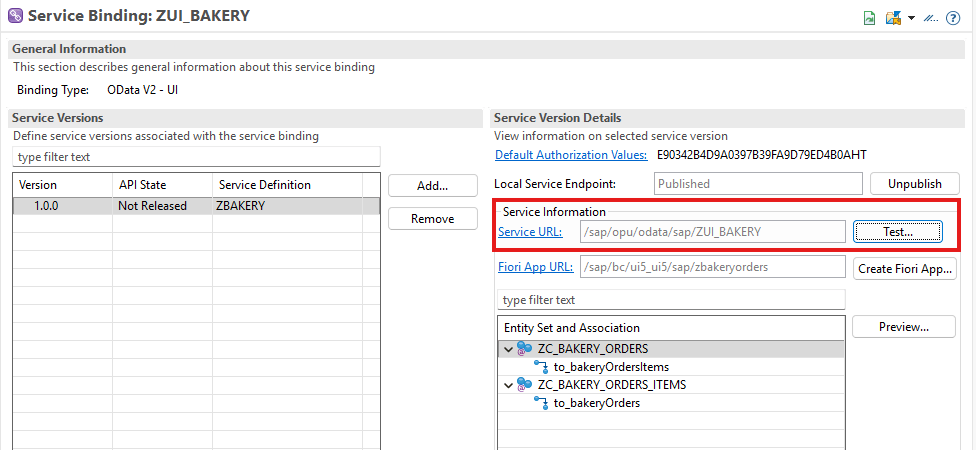
2. OData et Fiori tests
We also created a Fiori application using the creation tool via ADT.
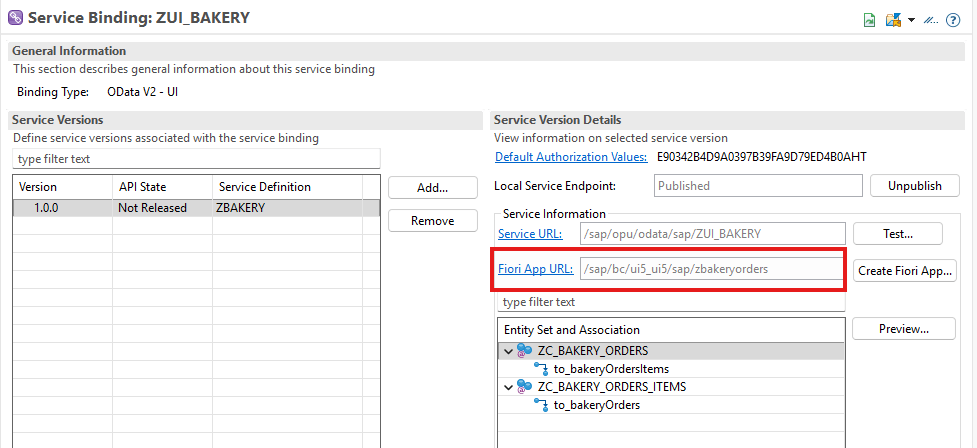
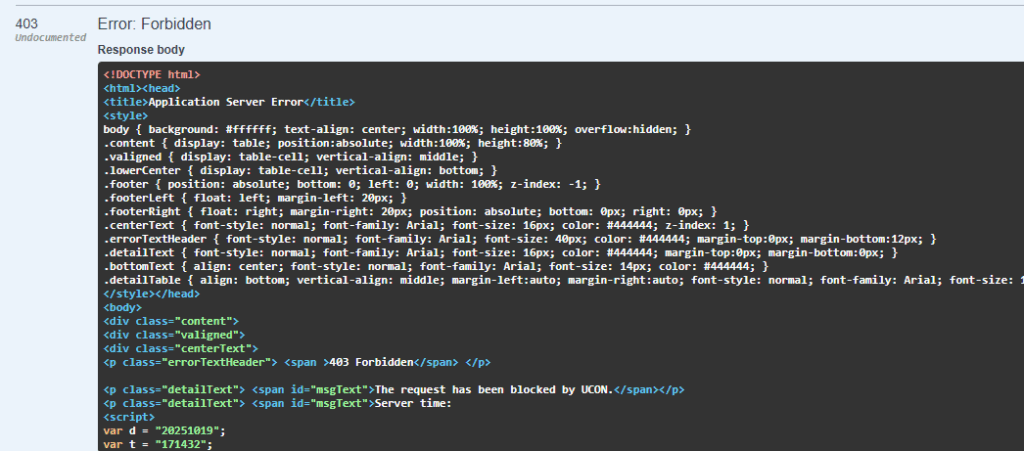
However, it appears that the construction trial is experiencing some issues at the moment. We will update the article once SAP has made the necessary corrections.
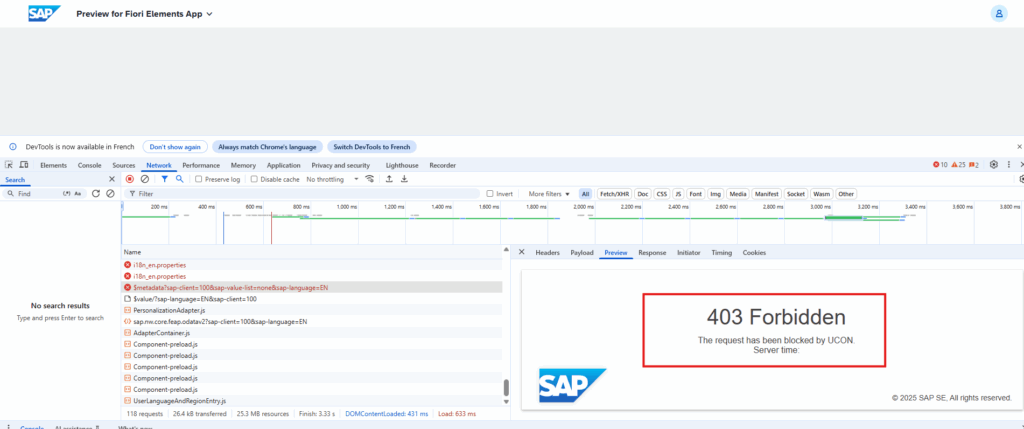
Same with swagger:
Conclusion
You can now use CDS table entities as RAP objects for all CRUD operations.
There are still a few details to be added to this new feature, but it won’t be long.
